Nolans East Project (LREE)

The Nolans East Project is prospective for light rare earths and is located only 15kms east of Arafura’s (ASX.ARU) 56Mt NPV $1.011Bn Light Rare Earth deposit.
Project highlights
- Prospective for light rare earths and located only 15kms east of Arafura’s (ASX.ARU) 56Mt NPV $1.011Bn light rare earth deposit
- Project covers 380km² of the Arunta Province, analogous to Nolan’s Bore light rare earth deposit
- Project area hosts structural and geological “plumbing” providing key conduit to the formation of large scale rare earth deposits
- Excellent access along the Stuart Highway in the Northern Territory
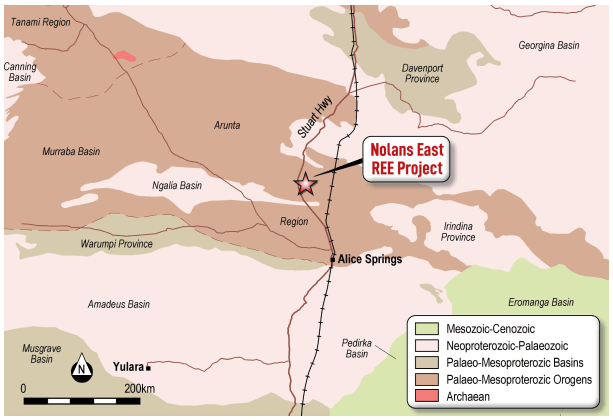
Excellent Infrastructure and Project Access
The Nolans East Project covers 380km² of the Arunta Province, analogous to Nolan’s Bore LREE deposit. It has excellent project access along the Stuart Highway in the Northern Territory.
First mover advantage adjacent to Nolan’s Bore
The Aileron Province is seeing a renewed focus of REE exploration, with Arafura Resources progressing towards construction and development of the Nolans Bore mine and recent pegging rush by explorers, including Arafura’s founding director Norman McCleary.
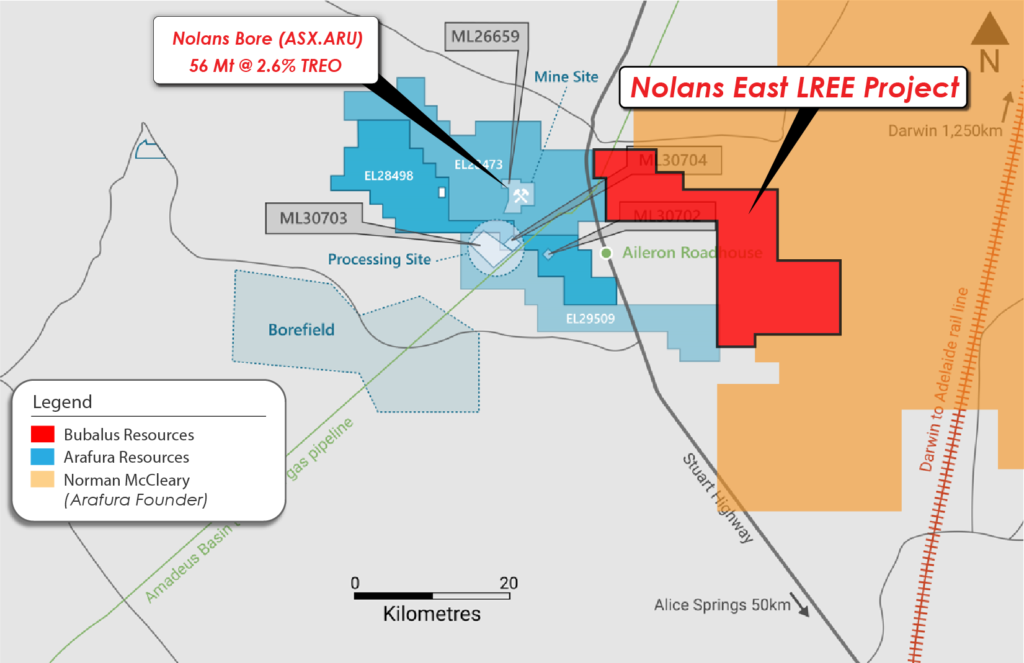
Right structural and geological “plumbing” provides key conduit to the formation of large scale REE deposits.
Fertile geochronology and stratigraphic settings
On a regional scale, within a 250km radius, the Nolans Bore deposit and other REE occurrences are spatially and structurally associated with a series of tin and tantalum pegmatites, and REE-bearing carbonatite/alkaline complexes.
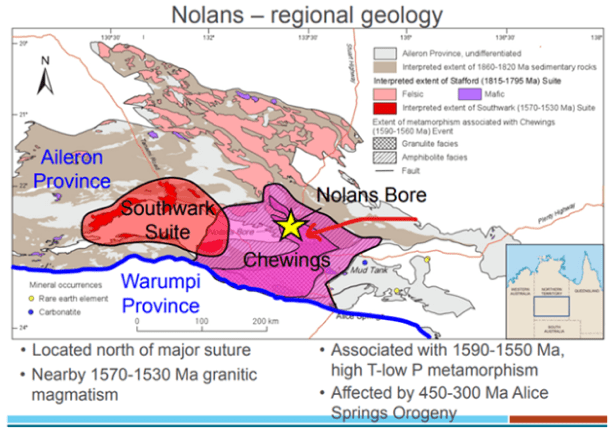
Structural faults into the unconformity are prime hosts of mineralisation
Geological processes leading to formation of Nolans Bore began with north-dipping subduction along the south margin of the Aileron Province resulting in alkaline low-degree partial melts.

Encouraging geochemical and geophysical correlations to Nolans Bore REE deposit
Prospective geological architecture acts as prime host unconformity REE deposits
The project area is underexplored for it’s hydrothermal stockwork vein-style Light Rare Earths (LREEs) potential. In particular, minerals including neodymium, and praseodymium are associated with these types of rare earths-phosphate-uranium-thorium (REE-P-U-Th) deposits such as Nolans Bore.
Follow up exploration will focus on identifying radiometric targets with signatures similar to Nolans Bore.
Surface geochemistry over TMI Magnetics displays strong correlation to Nolans Bore
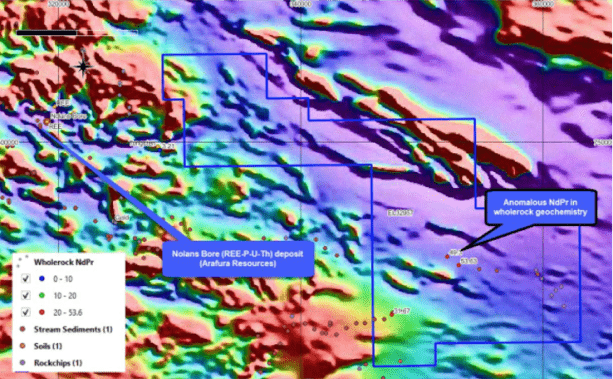
Kalahari Copper Belt in the Northern Territory?
Rio Tinto Geochemisty sampling and RAB Drilling (1997)
